C2A: Crowd Consensus Analytics for Virtual Colonoscopy
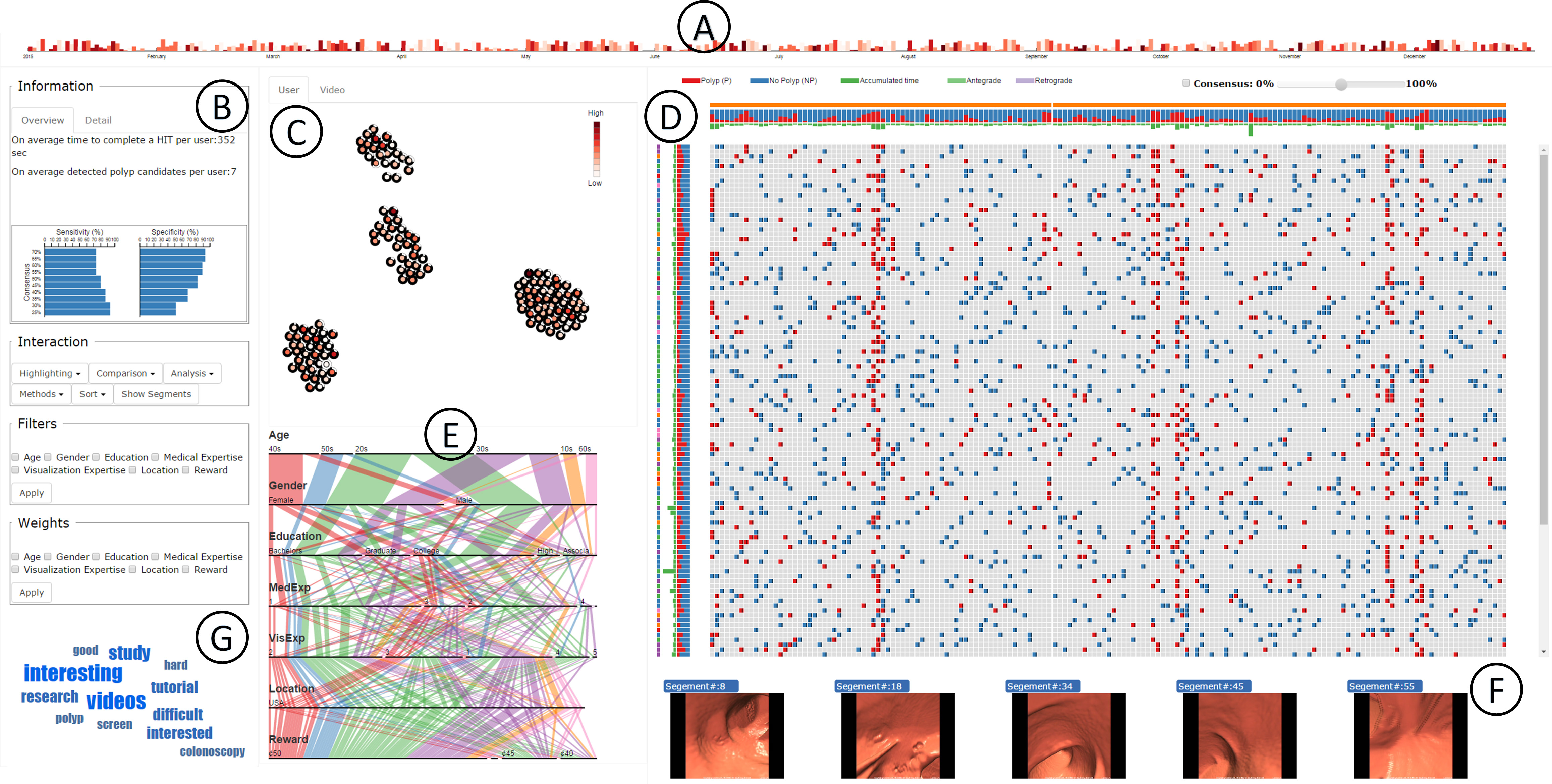
The C2A system includes (A) Timeline Filtering View for selecting datasets within a specified time interval,
(B) Aggregated Textual Information for displaying a textual summary of the crowd statistics and application specific performance,
(C) Similarity View for displaying the overlap and Euclidean distance metric of the crowd demographics and video segment statistics,
(D) Consensus Map for displaying the crowd consensus on polyp and polyp-free (benign) video segments along with aggregated crowd accuracy and timing,
(E) Crowd View for displaying crowd demographics and rewards, (F) Video Segments View for displaying selected video segments, and (G) Word Cloud displaying keywords from user comments.
Abstract
We present a medical crowdsourcing visual analytics platform called C2A to visualize, classify and filter crowdsourced clinical data.
More specifically, C2A is used to build consensus on a clinical diagnosis by visualizing crowd responses and filtering out anomalous activity.
Crowdsourcing medical applications have recently shown promise where the non-expert users (the crowd) were able to achieve accuracy similar to the medical experts.
This has the potential to reduce interpretation/reading time and possibly improve accuracy by building a consensus on the findings beforehand and letting the medical experts make the final diagnosis.
In this paper, we focus on a virtual colonoscopy (VC) application with the clinical technicians as our target users, and the radiologists acting as consultants and classifying segments as benign or malignant.
In particular, C2A is used to analyze and explore crowd responses on video segments, created from fly-throughs in the virtual colon.
C2A provides several interactive visualization components to build crowd consensus on video segments, to detect anomalies in the crowd data and in the VC video segments, and finally,
to improve the non-expert user's work quality and performance by A/B testing for the optimal crowdsourcing platform and application-specific parameters.
Case studies and domain experts feedback demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework in improving workers' output quality, the potential to reduce the radiologists' interpretation time,
and hence, the potential to improve the traditional clinical workflow by marking the majority of the video segments as benign based on the crowd consensus.
Publications
-
"C2A: Crowd Consensus Analytics for Virtual Colonoscopy"
-
"Crowdsourcing for Identification of Polyp-Free Segments in Virtual Colonoscopy Videos"
Video